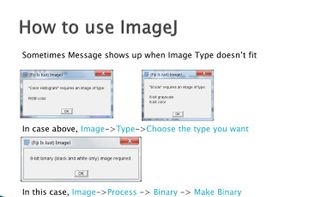
ImageJ is a public domain, Java-based image processing program developed at the National Institutes of Health. ImageJ was designed with an open architecture that provides extensibility via Java plugins and recordable macros.
Drishti is described as 'Open-source scientific visualisation software been developed with its end use in mind: ie. visualising volumetric data, such as tomography data, electron-microscopy data, etc' and is an app in the education & reference category. There are six alternatives to Drishti for a variety of platforms, including Windows, Linux, Web-based, Mac and Android apps. The best Drishti alternative is ImageJ, which is both free and Open Source. Other great apps like Drishti are Fiji, RadiAnt DICOM Viewer, Aeskulap and postDICOM - Free DICOM Viewer.
ImageJ is a public domain, Java-based image processing program developed at the National Institutes of Health. ImageJ was designed with an open architecture that provides extensibility via Java plugins and recordable macros.

Fiji is an image processing package—a "batteries-included" distribution of ImageJ, bundling a lot of plugins which facilitate scientific image analysis.
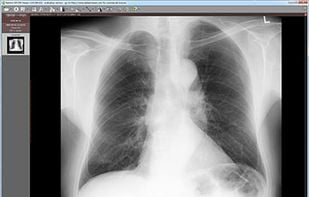
DICOM viewer. RadiAnt is a DICOM viewer for medical images designed to provide you with a unique experience. With its intuitive interface and unrivaled performance, you'll never look back.
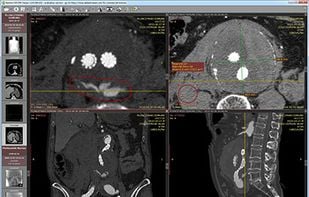
Aeskulap is a medical image viewer capable to load a series of special images stored in the DICOM format for review, query and fetch DICOM images from archive nodes (also called PACS) over the network.
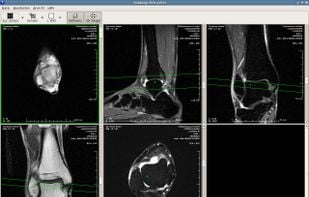
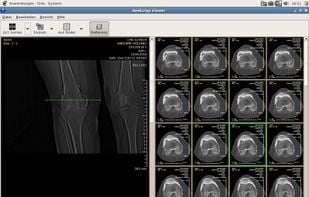
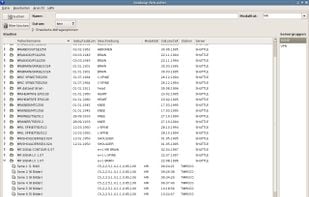
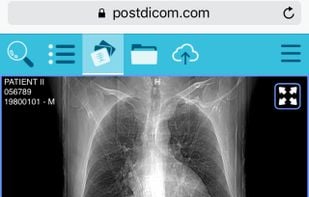
postDICOM is a cloud-based DICOM Viewer and clinical documents viewer. You can upload DICOM files and clinical documents using web browsers. You can upload and view your DICOM files from PCs(Windows, MacOS, Linux), tablets and phones(IOS and Android).
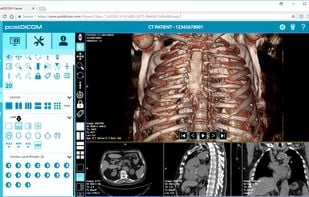
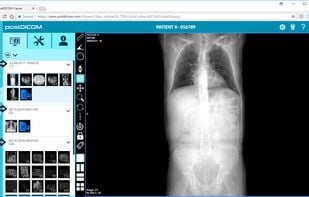
Data loaded in IDV (IMAIOS DICOM Viewer) isn't uploaded on the network to ensure storage safety and security of personal health information of the patients (excluding use of sharing features).